-
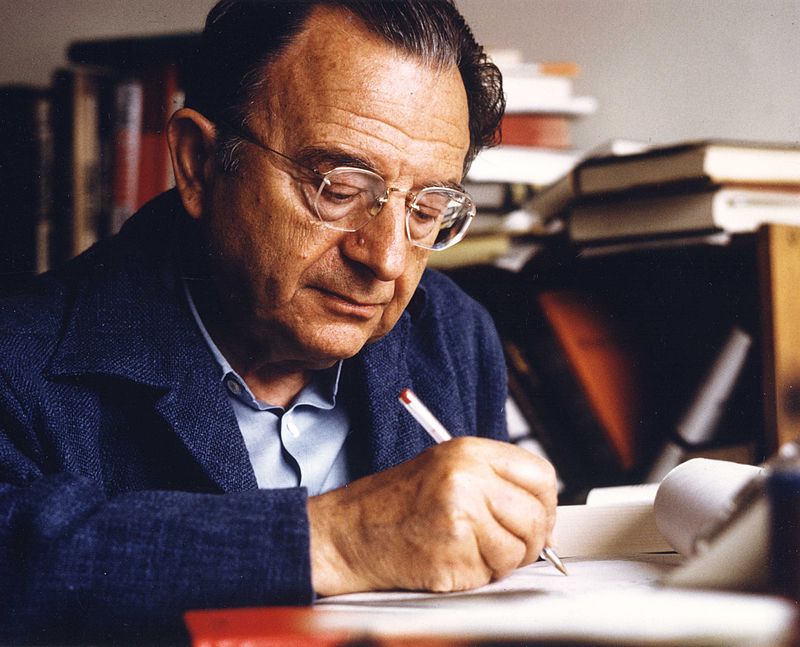

Erich Fromm’s The Art of Loving reframes love as an art requiring knowledge and practice rather than a mere emotion. It explores defining elements of love and critiques the commodification of relationships in capitalist societies. Despite its limitations regarding gender and contemporary forms of love, it remains a pivotal work linking personal and social transformation.
-

Sebastian Smee’s Paris in Ruins explores the cultural history of post-Franco-Prussian War Paris, highlighting the interplay of art, politics, and memory. While emphasizing aesthetic dimensions, it occasionally overlooks structural political factors and ordinary Parisians’ perspectives. The book illuminates how destruction informs cultural identity and collective memory, offering valuable insights for scholars and general readers alike.
-

Felix Morrow’s “Revolution and Counter-Revolution in Spain” provides a critical Marxist analysis of the Spanish Civil War, arguing that the Spanish proletariat had potential power which was undermined by reformist leadership. Morrow’s work highlights the dangers of class collaboration and emphasizes the need for revolutionary mobilization to confront authoritarianism and capitalist democracy.
-

Bryan Magee’s The Philosophy of Schopenhauer is a comprehensive and clear study of Schopenhauer’s thought, emphasizing his influence on Western philosophy. Magee adeptly contextualizes Schopenhauer’s ideas while making complex concepts accessible. The work’s interdisciplinary relevance and critical engagement with Schopenhauer’s limitations make it an essential read for scholars and students alike.
-

Ted Grant’s Selected Works, Vol. One presents his analyses of Stalinism and the Soviet Union’s class nature, emphasizing “proletarian Bonapartism.” Edited by Steve Iverson, this volume merges historical case studies with theoretical clarity, making it relevant for contemporary Marxist debates. However, it has limitations in empirical scope and cultural analysis.
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.