Communism
-
Contemporary Marxist theorists envision a democratic, participatory socialist planned economy focused on human needs rather than profit. With technology facilitating coordination without markets, resources are allocated through collective decision-making, emphasizing ecological sustainability and social welfare. This approach fosters empowerment, equality, and genuine democracy, seeking to reshape society for a more just future.
-

Leon Trotsky’s The Revolution Betrayed critiques the Soviet Union’s deviation from revolutionary ideals under Stalin. Published in 1937 and reissued in 2015, it analyzes the rise of bureaucracy and predicts the USSR’s collapse due to systemic issues. Trotsky’s insights on democracy and governance remain relevant for contemporary discourse in political and economic contexts.
-
The essay explores the evolving role of money in a future socialist society, building on Marxist theory. It argues that money, as a medium of exploitation under capitalism, would eventually wither away or transform in socialism, leading to direct social production and distribution. Initial transitional phases may involve labor vouchers, but these too would vanish…
-

Karl Marx’s economic theories emphasize class struggle as the driving force behind societal change and historical evolution. Central concepts include the labor theory of value, surplus value, and historical materialism, which illustrate the antagonistic relationship between the bourgeoisie and proletariat. This conflict reflects broader socio-economic dynamics, ultimately predicting a revolutionary transition towards socialism and communism.
-

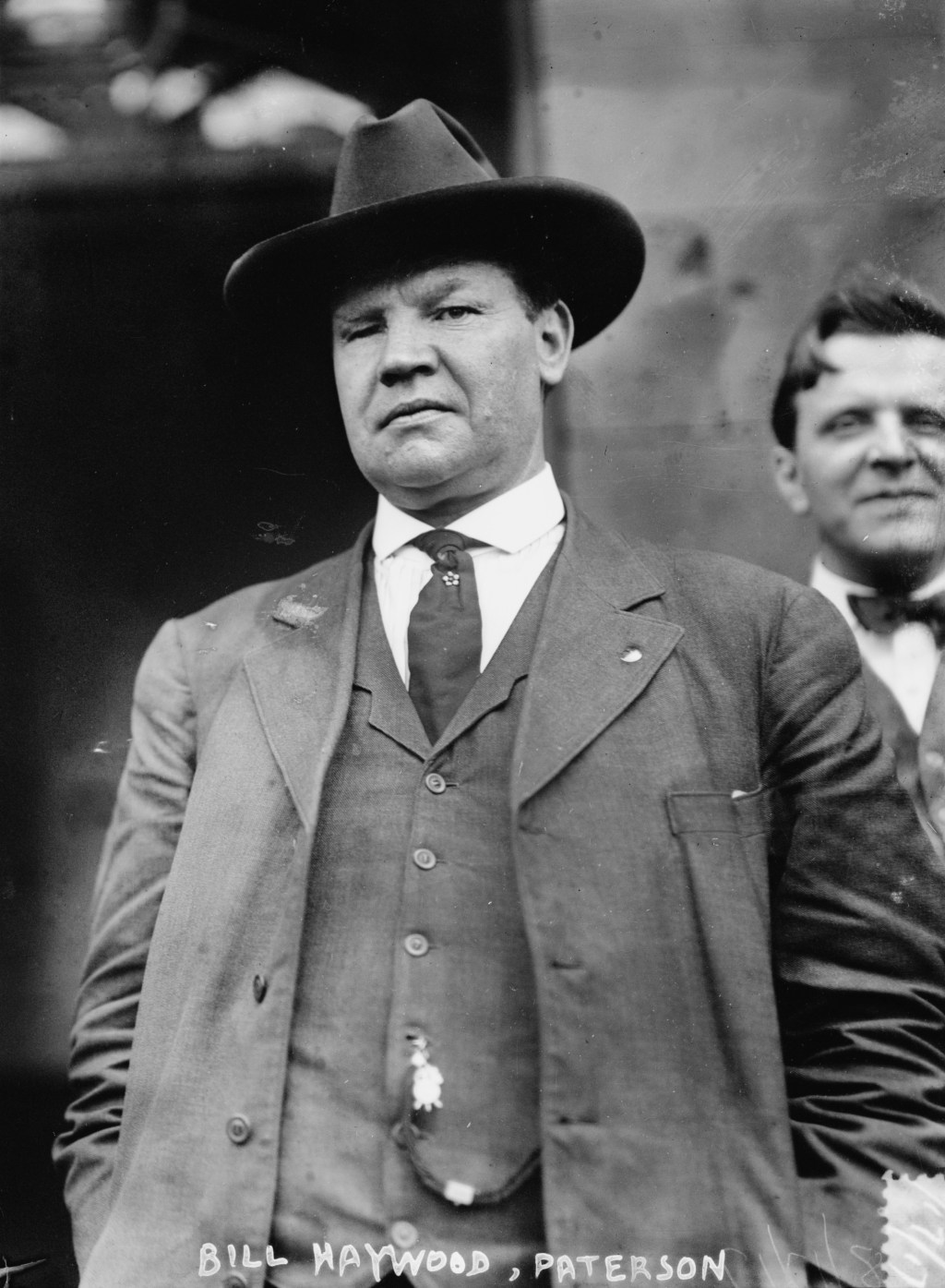
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), founded in 1905, championed radical labor rights against the conservative American Federation of Labor. Known as “Wobblies,” they aimed to unite all workers under “One Big Union.” Despite severe repression, their cultural impact and legacy of revolutionary activism continue to inspire modern labor movements.
-

Between 1920 and 1940, Soviet law enforcement evolved significantly under Marxist-Leninist ideology, serving the Communist Party’s revolutionary goals. Institutions like the Cheka and NKVD enforced state security through extensive surveillance and brutal repression, targeting class enemies and dissenters. This ideological framework shaped a coercive policing system that instilled fear and compliance in society.