-

The text explores the distinctions between determinism and fatalism. Determinism asserts that human actions are caused by preceding conditions, allowing for meaningful freedom, while fatalism posits that outcomes are preordained, rendering human efforts meaningless. Embracing determinism encourages responsibility and progress, while fatalism leads to passivity and despair.
-

The inquiry into whether the universe had a beginning captivates theologians, philosophers, and scientists. While religion offers a divine explanation, science presents the Big Bang theory. Both perspectives reveal our ignorance and underscore the limits of human understanding. Embracing doubt fosters wisdom and humility in exploring existence’s mysteries.
-

Dialectical materialism, rooted in Marxist philosophy, interprets societal change through material contradictions within economic systems. While acknowledging its limitations and critiques, this framework remains relevant in addressing modern challenges like climate change and digital monopolies. Embracing its insights, without rigid dogma, is essential for understanding and navigating our rapidly evolving world.
-

Nature exemplifies a dialectical reality where conflict drives progress and evolution. Rather than a static harmony, it embodies perpetual clashes that shape life systems. These contradictions create order from disorder and highlight humanity’s exploitation of nature, culminating in a precarious balance that demands new resolutions through inevitable struggle.
-

Wishing everyone a bold Happy New Year! Embrace the chance to move beyond the past and seize new opportunities. Leave behind trivial challenges and prepare for ambitious successes. May your hearts soar with passion, energy, and love as you embark on an extraordinary journey this year. Cheers to new beginnings!
-
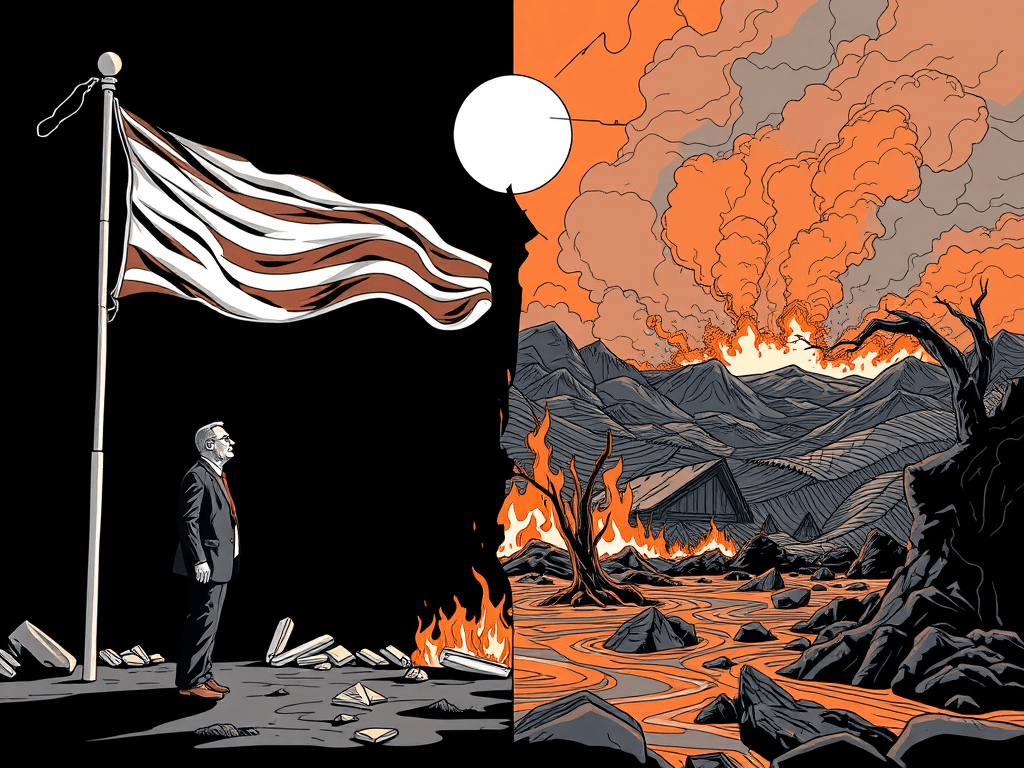
The year mirrored a struggle between democracy’s decay, climate change impacts, and geopolitical conflicts, emphasizing humanity’s fragility. While populist leaders gained traction, natural disasters loomed, and global peace remained elusive. Amidst this, hope persisted through scientific advancements and youth activism, urging collective accountability for a better future.
-
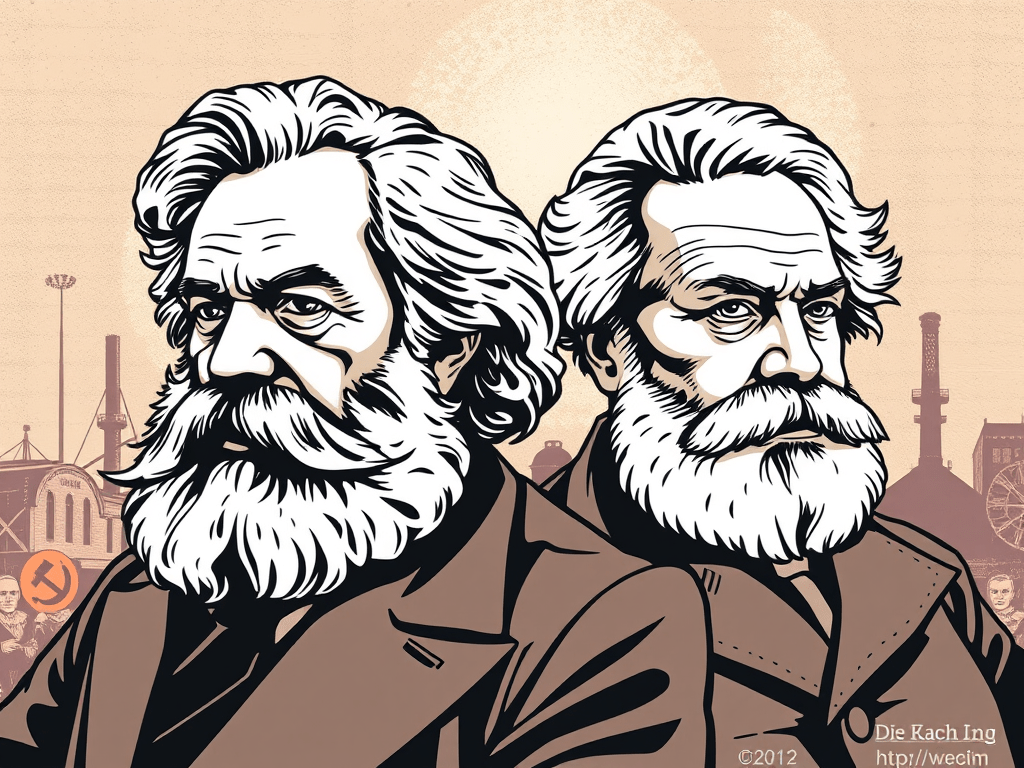
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels revolutionized political thought by emphasizing materialism and the dynamics of history rooted in economic realities. They critiqued utopian socialism, arguing capitalism’s inherent contradictions would lead to its downfall. Their insights into ideology became foundational for later critique, challenging society’s structures and urging responsibility in transforming the world.
-
Jolande Jacobi’s The Psychology of C.G. Jung serves as a comprehensive introduction to Jungian ideas, balancing clarity and depth. Published in 1942, it covers key concepts like the psyche structure, archetypes, and individuation. While not critically evaluative, it effectively illustrates Jung’s methods and remains an essential resource for understanding analytical psychology.
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.

